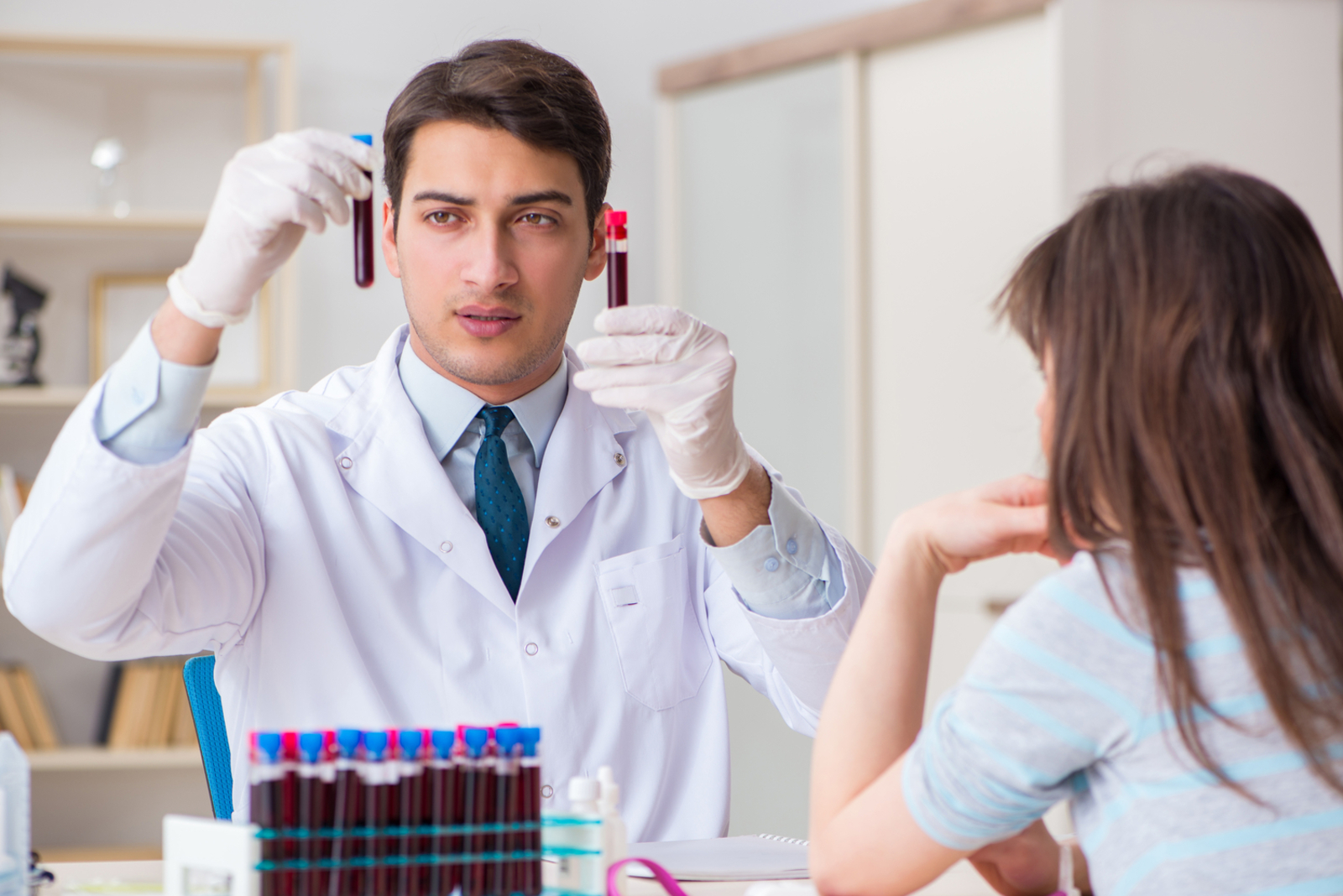
Blood Disorders Risk Factors
If you have an issue with your blood, it can impact your health as a whole—conditions like anemia, blood clotting, and hemophilia are examples of blood disorders. In order to receive a diagnosis, you will likely require blood samples to be taken in order to evaluate red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelet tests. For example, hemoglobin tests, hematocrit tests, reticulocyte counts, platelet counts, peripheral blood smears, or a complete blood count are examples of tests that may be conducted. Certain circumstances put you at a higher risk for blood disorders, which we identify here:
1. Lifestyle factors
Certain lifestyle factors, including smoking, excessive alcohol intake, and a poor diet can contribute to the development of certain blood disorders. In particular, such lifestyle factors are more associated with the development of blood disorders related to the cardiovascular system; for example, blood clotting disorders. Be sure to eat nutritious foods (especially those high in iron, vitamin B12, and folate), avoid smoking, and avoid drinking alcohol or only drink in moderation.
2. Environmental factors
If you have been exposed to toxins, radiation, or certain chemicals, this can increase your risk of developing blood disorders. Benzene, pesticides, lead, solvents, and ionizing radiation (x-rays, radiation therapy, nuclear accidents, etc.) are examples of environmental factors that can damage blood cells, potentially resulting in blood disorders.
3. Family history
Blood disorders such as hemophilia and thalassemia have a genetic component, meaning if someone in your family has or had a blood disorder, it increases your risk of development as well.
4. Autoimmune disorders
Certain autoimmune disorders, like Lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, have the ability to cause the immune system to attack blood cells. This can result in conditions like autoimmune hemolytic anemia or immune thrombocytopenia.
5. Medications and treatments
Understanding the potential side effects of certain medications and treatment is crucial, as in some cases, they can have adverse effects on the blood. For example, certain meds, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy can lead to conditions like anemia or a low platelet count.
Risk factors can vary widely, and not everyone with these risk factors will end up developing a blood disorder. However, it’s important to be aware of such factors in order to facilitate healthy change in your lifestyle choices or speak to your doctor if you have any concerns about your risk of developing a blood disorder.